What is Spread Betting?
The basics of spread betting are that you are presented with a range of values. As a punter, you have to bet whether the outcome is going to be above or below a given value. The world of spread betting is a much-varied thing, all of which we will break down in this guide.
Spread betting can be a high-risk mode of betting. That is because you are not just looking at a fixed risk on a simple outcome. The more that you are wrong in a spread bet, then the more costly it is going to be for you.
While spread betting is in practice quite distinct from gambling, the returns that can be afforded by spread betting are easily comparable, thanks to this multiplying effect – known as ‘leverage'. Leverage is arguably the most central feature of spread betting, and the one highlight that makes it so popular. Because markets can move by a wide range of points over the space of a day, immediate returns can. The Basics of Spread Betting Explained. April 28, 2016 by DivHut. The following is a sponsored blog post: Spread betting can be a powerful way to increase the diversification of your side hustle and earn a significant amount of money without necessarily being concerned about market conditions. Whether a bullish or bearish sentiment dominates. Get an introduction to spread betting; learn what the benefits & risks are, and see how to open a spread bet account with Finspreads. Discover the alternative to shares trading.
How does Spread Betting Work?
Spread betting actuallyworks in different ways, because there are different variations of it anddifferent formats. For example, there is a great difference between sportsspread betting in the US and in the UK.
You have points spreadbetting, over/under and financials as variations of spread betting. While wewill cover them all in this guide, the most important thing to mention is howspread betting works in the UK. It is possible that you can lose more than you stakein spread betting.
It becomes about accuracy rather than picking a winner. Spread betting is more fluid, more variable than rigid win markets. Let's say we are looking at Real Madrid v Barcelona win single in regular sports betting. You have three options, a home win, away win, or a draw in the outright market.
You know what stake youare playing. You know your exact risk. You know your exact potential profit.With spread betting, well, you don't know the potential win. That's because youare betting one unit stake for every point, goal or whatever it is, above thevalue of the spread bet you have made.
Let's explain.
UK Spread Betting
Spread betting has risk,just as all types of wagers do. However, spread betting has a higher risk thanjust regular straight-up bets. If you have placed a wager on Man City -1handicap with a 10 stake then you know that the total amount that you arerisking is 10.
That's it. If City don'twin by a two goal margin you lose. The risk is fixed. The risk is NOT fixed in spreadbetting. That is a crucial thing to put in your head and let linger there.
In fact, spread bettingcan get pretty hairy. It all involves buying and selling.
Buying and Selling theSpread
You are not dealing with odds as in regular betting. Instead with spread betting, you can Buy or Sell on the spread. Whatever the designated spread is, you would either Buy the high number or Sell the low number.
| Spread = 6-7 Corners | Buy at 7 | Sell at 6 |
|---|---|---|
| You expect MORE than 7 corners to happen | You expect LESS than 6 corners to happen |
That, in a nutshell is what buying or sellingon the spread means. But where does the stake come into this? Let's carry onwith this example, of 6-7 corners. You Buy in with a 10 stake at 7 corners.

Remember you always Buy the high number in aspread. That would mean that for every corner above 7 that happened in thegame, you would earn 10. So if there were 10 corners in total in the match,that's a 30 profit.
Buying 7 Corners (win):
| BUY 7 Corners | Total Corners | +/- Difference | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 stake | 10 corners | +3 | 3 x 10 = 30 WIN |
Your stake is linked to the unit of the degree of correctness if you like. The more right you are, the bigger the payout.
However, if the game ended with less than 7corners in the match, then for every corner less than 7 you would LOSE 10. Soif there were only 2 corners in the match, you would lose 50.
So in this type of spread betting (there are fixed spread bets that don't work this way as you will see in this guide), you can lose more than you stake.
Buying 7 Corners (loss):
| BUY 7 Corners | Total Corners | +/- Difference | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 stake | 2 corners | -5 (7 - 2) | 5 x 10 = 50 LOSS |
But if from the offset you thought that thegame was going to produce fewer than 6 corners anyway, then you would haveapproached it a different way. You would Sell 6 corners.

For every corner under that spread of 6, youwould claim a 10 win. However, for every corner over 6 that happened in thatgame, that would cost you 10.
Selling 6 Corners:
| SELL 6 Corners | Total Corners | +/- Difference | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 stake | 2 corners | +4 (6 - 2) | 4 x 10 = 40 WIN |

So that is the big risk with spread bettingand why it's not to be taken lightly. You will find this type of spread bettingmore commonly in Financials. But just to vary off slightly, let's look atspread betting and what it means in the USA.
US Spread Betting
It is common practice to see points spread betting happening in US betting. Particularly on NFL football. Points spread betting is where the bookmaker gives one team an advantage and the other a disadvantage, in terms of margin of victory.
For example, New England Patriots -4.5 means that a backer who has placed a stake on them would need the Patriots to win by at least five points. This is a scenario where a stronger team, starts the game (virtually) with a -4.5 handicap on them.
So in order for the bet on them to win, they would have to cover the spread by winning by a five-point margin. If they were to win the match but only by two points, then the bet on them loses, even though the Pats won the match.
Dallas Cowboys +4.5 means that the backerwould need Dallas to not lose by a margin of more than four points. It isbasically a scenario where the bookmaker has given Dallas the advantage ofstarting the game with a 4.5 point lead.
So even if they were to lose the match 20-17 your bet on them would still win when you add on those 4.5 points to their score. That's straight forward points spread betting in the US. It's a fixed stake though, not the type of UK spread betting which will fluctuate.
Over/Under
Over/Under does fall into the category of spread betting only inasmuch as you are betting on a spread value. It's more of a Totals option than a spread bet really. This is just where instead of backing a team to cover a spread in a match, as in the above example, you are just targeting the total of points in a game.
This can be the total points in a game betweenthe two teams. Or the total points of one team only in the game. While you arein a sense trying to determine that an outcome reaches above (or under) a setspread value, it's not technically a spread bet.
The difference really is that risk goes backto being a set risk. A Totals bet like an Over/Under just takes a straightstake for set odds. The profit or loss isn't going to increase the further awayfrom the prediction that the total amount of points ends up at.
Financial Spreads
Spread betting in the UK is far less common in sports than it is on Financials. What exactly are Financials? This is where you do spread betting against things like the value of currency or the value of stocks.
As you may know, these are generally volatile things. Stocks go up, stocks go down, sometimes all depending on which way the wind is blowing. The same with currency, a piece of breaking news somewhere in the world can affect a currency's value halfway on the other side of the globe.
So what makes Financials betting so appealing? It is a big shift in value. Imagine that you have speculated on the share price of Company X. That company releases a new product that day, everybody loves them and their share value soars.
It will likely be a big gain as well, sothat's where a spread bet could pay off. But that is a best-case-scenarioexample and the real world isn't often like that. In fact, Financials bettingis very complex and very high risk.
It's estimated that almost 70% of investorslose money when trading spread bets. A 2009 report by the Times newspaperstated that it was around 1 in 10 spread betting traders that were profitablein the UK. That's how risky it can be.
Financials spreads, very basically is youdeciding which way a market is going to move.
Example of a Financials Spread:
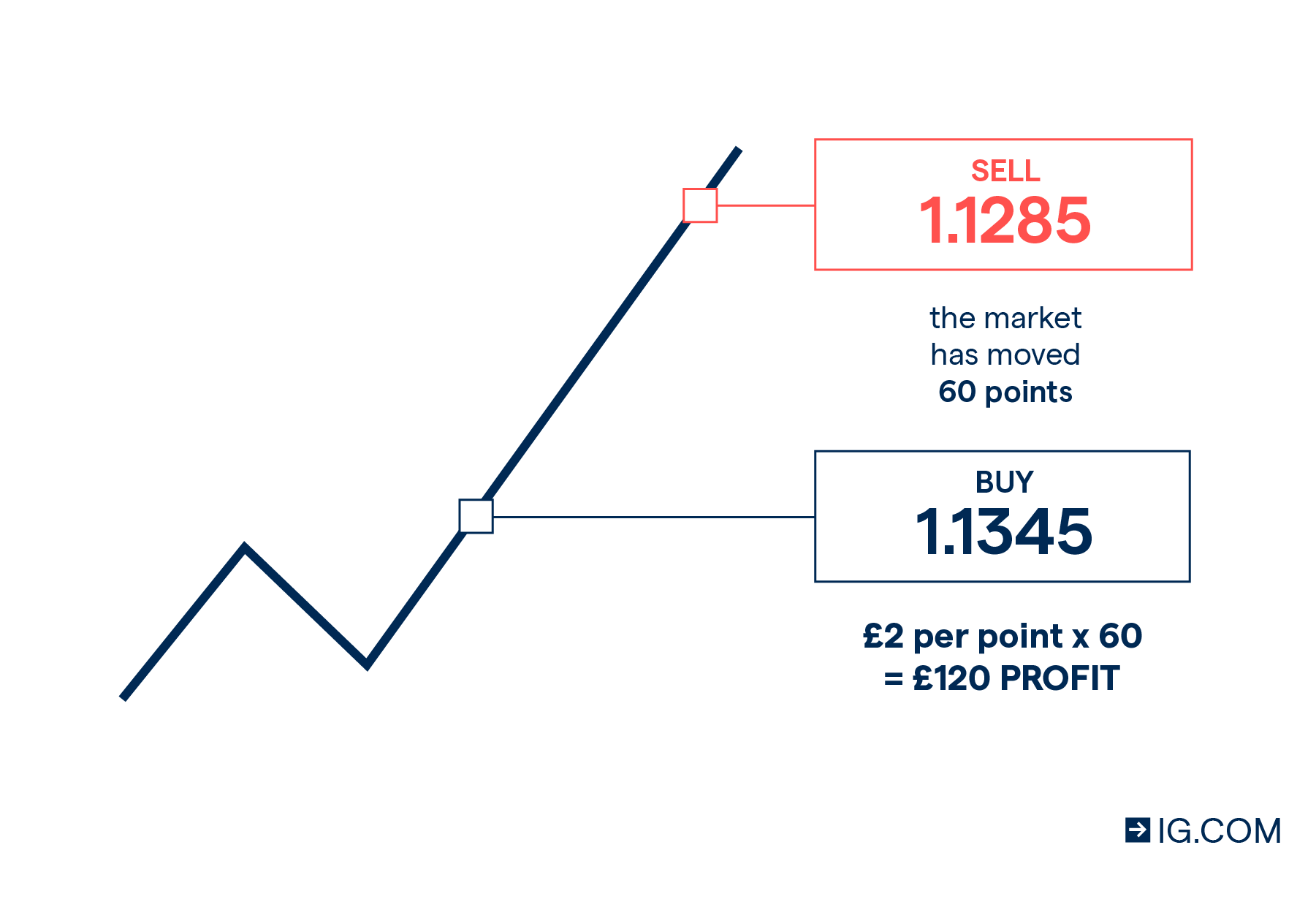
| Up↑ | ←Market Movement→ | Down↓ |
|---|---|---|
| 101p | 100p | 99p |
In this example the spread is the margin between the Up and Down value. It's not called Up and Down though, it's called BUY and SELL:
| Up↑ | ←Market Movement→ | Down↓ |
|---|---|---|
| 101p | 100p | 99p |
| If you think that the market is going to go up, you BUY at the top of the spread. | If you think that the market is going to go down, you SELL at the bottom of the spread. |
Then what happens? Well you wait and see whathappens to the market. You can open and close bets within a 24 hour periodgenerally.
If you Buy and the market goes up, you getyour unit of stake multiplied by however many points the market went up abovethe price at which you bought the spread.
If you buy and the market goes down, you willlose a unit of stake multiplied by however many points the market finishesbelow the price at which you bought at. It's simply a case of vice-versa if youhad done a Sell option to start with.
Note in that very simpleformula, the glaring variable. Profit or loss. You do not know the complete total of what you are risking until themarket is done. A major crash in a market after you have done a Buy optionexpecting it to go up could cost a fortune.
Financials betting is awhole different beast, a world away from regular sports betting. It's complexand it has a whole range of specialist tools to use, as well as specialistbrokers.
What are Brokers?
Brokers in Financialspread betting are a version of bookmakers. They are the middleman throughwhich you strike your bets. Only instead of being called a bookmaker, whichtechnically they are not, they are called Brokers. They are the ones whichallow you to go and speculate on all of the market fluctuations.
Spread BettingCollateral
We have already and willcontinue to do so, speak of the risks of spread betting. There is no fixed loss(although there are limits). It's all just random on how the markets willreact, and you are never certain of that. Now let's put collateral intoperspective.
You bet on the value ofthe Bank of NeverNeverland which is currently at 400p. The spread, therefore,is to Buy at 401p or Sell at 399p. We go with a 10 stake, which means that ishow much we will win for every penny that the market goes up above the 401p atwhich we bought in.
But what is theworst-case scenario here? That would be if the value of the Bank ofNeverNeverland went down to a big fat zero. So that would mean a drop of 400p,its full value. 400 x 10 per unit = 4000 maximum loss that could happen fromour bet.
That's substantial. Notlikely to happen, but that's called the Collateral. An extreme example of it.But it's to illustrate a point that you are going to need to have collateral inyour account to place the initial bet.
You have to be able tocover potential losses. This won't always be at 100% depending on the type offinancials bet you are playing. It's more realistically going to be 5% of 10%on your total exposure (the max you can lose). Why? Because of Leverage. Readon.
Spread Betting Leverage
This is another of those common terms. A slightly more complex one and it follows on from collateral. Teacup Trains is at 500p. You want to buy-in with a 1 stake. But what about the big 500 collateral if the value goes down to zero (full exposure)?
Well, the Spread Bettingfirm is only asking for a 10% margin to make this bet (so 50). The rest (450)is loaned to you by the firm. A good outcome is that the value goes up 200points and you trade out with 200 profit, all from that 50 deposit risk of yourown money.
If things go badly, and the value goes down, you are out of your 50 stakes and if it all tanks to zero, you would owe your operator the 450 they loaned you.
The thing with leverage is that if the market does move in your favour it means that you never had to physically come up with the full 500 value of the exposure. If you wanted to go to a Broker and buy 100 shares at the same value, you would need that full 500.
So basically summed up, spread betting leverage allows you to put up a small margin of a big spread bet exposure value. For example, if the full exposure was 20,000 a 10% margin means you put up 2,000 deposit on your bet.
What's the differencebetween a spread and a money line?
A spread and a moneyline are different things. The spread is as mentioned above, where a bookmakersets out a spread, a value that needs to be covered, like the New EnglandPatriots -4.5.
The important thing tonote is that the result on the pitch is not definitive for the bet. It's allabout the points spread. A Moneyline in contrast, is a fixed-odds bet, just astraight-up bet on the winner of the match.
You will see somethinglike New York Giants -150 and Miami Dolphins +125. On the Moneyline, these arenot point spreads, these are odds. The minus sign represents the favourite, theplus sign represents the underdogs.

The -150 on the Giants means that you would have to bet 100 to win 150.
The +125 on the Dolphins means that you would win 125 for every 100 bet.
FAQ's
Is Spread Betting profitable?
You can lose more than you stake with spread betting. There are of course ways to be profitable in spread betting. Chasing big returns though comes with high risk.
A good trader may target 1% profit in a month. It is possible but not easy. Strategies promising to earn you between 100 and 2000 a month are not that realistic.
Big sums like than means that you are facing some big exposures, especially if you are only taking 1% profit on speculations.
The US version of spread betting is a lot more approachable. Things like points spreads are just regular sports betting wrapped up differently.
What happens if you tie the spread?
You get your money back. This scenario is called a Push. A push is a very common term and a very common occurrence in spread betting.
Note that a push can never happen where you have half points. Point spread payout table. If you have Over 3.5 goals in a soccer match, no team is going to score half of a goal.
So the inclusion of the half goal means that a result (win or loss) will happen on the bet. However, you will see straight whole-number spread options too. Maybe it is a simple -4 on the Atlanta Falcons to win.

Remember you always Buy the high number in aspread. That would mean that for every corner above 7 that happened in thegame, you would earn 10. So if there were 10 corners in total in the match,that's a 30 profit.
Buying 7 Corners (win):
| BUY 7 Corners | Total Corners | +/- Difference | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 stake | 10 corners | +3 | 3 x 10 = 30 WIN |
Your stake is linked to the unit of the degree of correctness if you like. The more right you are, the bigger the payout.
However, if the game ended with less than 7corners in the match, then for every corner less than 7 you would LOSE 10. Soif there were only 2 corners in the match, you would lose 50.
So in this type of spread betting (there are fixed spread bets that don't work this way as you will see in this guide), you can lose more than you stake.
Buying 7 Corners (loss):
| BUY 7 Corners | Total Corners | +/- Difference | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 stake | 2 corners | -5 (7 - 2) | 5 x 10 = 50 LOSS |
But if from the offset you thought that thegame was going to produce fewer than 6 corners anyway, then you would haveapproached it a different way. You would Sell 6 corners.
For every corner under that spread of 6, youwould claim a 10 win. However, for every corner over 6 that happened in thatgame, that would cost you 10.
Selling 6 Corners:
| SELL 6 Corners | Total Corners | +/- Difference | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 stake | 2 corners | +4 (6 - 2) | 4 x 10 = 40 WIN |
So that is the big risk with spread bettingand why it's not to be taken lightly. You will find this type of spread bettingmore commonly in Financials. But just to vary off slightly, let's look atspread betting and what it means in the USA.
US Spread Betting
It is common practice to see points spread betting happening in US betting. Particularly on NFL football. Points spread betting is where the bookmaker gives one team an advantage and the other a disadvantage, in terms of margin of victory.
For example, New England Patriots -4.5 means that a backer who has placed a stake on them would need the Patriots to win by at least five points. This is a scenario where a stronger team, starts the game (virtually) with a -4.5 handicap on them.
So in order for the bet on them to win, they would have to cover the spread by winning by a five-point margin. If they were to win the match but only by two points, then the bet on them loses, even though the Pats won the match.
Dallas Cowboys +4.5 means that the backerwould need Dallas to not lose by a margin of more than four points. It isbasically a scenario where the bookmaker has given Dallas the advantage ofstarting the game with a 4.5 point lead.
So even if they were to lose the match 20-17 your bet on them would still win when you add on those 4.5 points to their score. That's straight forward points spread betting in the US. It's a fixed stake though, not the type of UK spread betting which will fluctuate.
Over/Under
Over/Under does fall into the category of spread betting only inasmuch as you are betting on a spread value. It's more of a Totals option than a spread bet really. This is just where instead of backing a team to cover a spread in a match, as in the above example, you are just targeting the total of points in a game.
This can be the total points in a game betweenthe two teams. Or the total points of one team only in the game. While you arein a sense trying to determine that an outcome reaches above (or under) a setspread value, it's not technically a spread bet.
The difference really is that risk goes backto being a set risk. A Totals bet like an Over/Under just takes a straightstake for set odds. The profit or loss isn't going to increase the further awayfrom the prediction that the total amount of points ends up at.
Financial Spreads
Spread betting in the UK is far less common in sports than it is on Financials. What exactly are Financials? This is where you do spread betting against things like the value of currency or the value of stocks.
As you may know, these are generally volatile things. Stocks go up, stocks go down, sometimes all depending on which way the wind is blowing. The same with currency, a piece of breaking news somewhere in the world can affect a currency's value halfway on the other side of the globe.
So what makes Financials betting so appealing? It is a big shift in value. Imagine that you have speculated on the share price of Company X. That company releases a new product that day, everybody loves them and their share value soars.
It will likely be a big gain as well, sothat's where a spread bet could pay off. But that is a best-case-scenarioexample and the real world isn't often like that. In fact, Financials bettingis very complex and very high risk.
It's estimated that almost 70% of investorslose money when trading spread bets. A 2009 report by the Times newspaperstated that it was around 1 in 10 spread betting traders that were profitablein the UK. That's how risky it can be.
Financials spreads, very basically is youdeciding which way a market is going to move.
Example of a Financials Spread:
| Up↑ | ←Market Movement→ | Down↓ |
|---|---|---|
| 101p | 100p | 99p |
In this example the spread is the margin between the Up and Down value. It's not called Up and Down though, it's called BUY and SELL:
| Up↑ | ←Market Movement→ | Down↓ |
|---|---|---|
| 101p | 100p | 99p |
| If you think that the market is going to go up, you BUY at the top of the spread. | If you think that the market is going to go down, you SELL at the bottom of the spread. |
Then what happens? Well you wait and see whathappens to the market. You can open and close bets within a 24 hour periodgenerally.
If you Buy and the market goes up, you getyour unit of stake multiplied by however many points the market went up abovethe price at which you bought the spread.
If you buy and the market goes down, you willlose a unit of stake multiplied by however many points the market finishesbelow the price at which you bought at. It's simply a case of vice-versa if youhad done a Sell option to start with.
Note in that very simpleformula, the glaring variable. Profit or loss. You do not know the complete total of what you are risking until themarket is done. A major crash in a market after you have done a Buy optionexpecting it to go up could cost a fortune.
Financials betting is awhole different beast, a world away from regular sports betting. It's complexand it has a whole range of specialist tools to use, as well as specialistbrokers.
What are Brokers?
Brokers in Financialspread betting are a version of bookmakers. They are the middleman throughwhich you strike your bets. Only instead of being called a bookmaker, whichtechnically they are not, they are called Brokers. They are the ones whichallow you to go and speculate on all of the market fluctuations.
Spread BettingCollateral
We have already and willcontinue to do so, speak of the risks of spread betting. There is no fixed loss(although there are limits). It's all just random on how the markets willreact, and you are never certain of that. Now let's put collateral intoperspective.
You bet on the value ofthe Bank of NeverNeverland which is currently at 400p. The spread, therefore,is to Buy at 401p or Sell at 399p. We go with a 10 stake, which means that ishow much we will win for every penny that the market goes up above the 401p atwhich we bought in.
But what is theworst-case scenario here? That would be if the value of the Bank ofNeverNeverland went down to a big fat zero. So that would mean a drop of 400p,its full value. 400 x 10 per unit = 4000 maximum loss that could happen fromour bet.
That's substantial. Notlikely to happen, but that's called the Collateral. An extreme example of it.But it's to illustrate a point that you are going to need to have collateral inyour account to place the initial bet.
You have to be able tocover potential losses. This won't always be at 100% depending on the type offinancials bet you are playing. It's more realistically going to be 5% of 10%on your total exposure (the max you can lose). Why? Because of Leverage. Readon.
Spread Betting Leverage
This is another of those common terms. A slightly more complex one and it follows on from collateral. Teacup Trains is at 500p. You want to buy-in with a 1 stake. But what about the big 500 collateral if the value goes down to zero (full exposure)?
Well, the Spread Bettingfirm is only asking for a 10% margin to make this bet (so 50). The rest (450)is loaned to you by the firm. A good outcome is that the value goes up 200points and you trade out with 200 profit, all from that 50 deposit risk of yourown money.
If things go badly, and the value goes down, you are out of your 50 stakes and if it all tanks to zero, you would owe your operator the 450 they loaned you.
The thing with leverage is that if the market does move in your favour it means that you never had to physically come up with the full 500 value of the exposure. If you wanted to go to a Broker and buy 100 shares at the same value, you would need that full 500.
So basically summed up, spread betting leverage allows you to put up a small margin of a big spread bet exposure value. For example, if the full exposure was 20,000 a 10% margin means you put up 2,000 deposit on your bet.
What's the differencebetween a spread and a money line?
A spread and a moneyline are different things. The spread is as mentioned above, where a bookmakersets out a spread, a value that needs to be covered, like the New EnglandPatriots -4.5.
The important thing tonote is that the result on the pitch is not definitive for the bet. It's allabout the points spread. A Moneyline in contrast, is a fixed-odds bet, just astraight-up bet on the winner of the match.
You will see somethinglike New York Giants -150 and Miami Dolphins +125. On the Moneyline, these arenot point spreads, these are odds. The minus sign represents the favourite, theplus sign represents the underdogs.
The -150 on the Giants means that you would have to bet 100 to win 150.
The +125 on the Dolphins means that you would win 125 for every 100 bet.
FAQ's
Is Spread Betting profitable?
You can lose more than you stake with spread betting. There are of course ways to be profitable in spread betting. Chasing big returns though comes with high risk.
A good trader may target 1% profit in a month. It is possible but not easy. Strategies promising to earn you between 100 and 2000 a month are not that realistic.
Big sums like than means that you are facing some big exposures, especially if you are only taking 1% profit on speculations.
The US version of spread betting is a lot more approachable. Things like points spreads are just regular sports betting wrapped up differently.
What happens if you tie the spread?
You get your money back. This scenario is called a Push. A push is a very common term and a very common occurrence in spread betting.
Note that a push can never happen where you have half points. Point spread payout table. If you have Over 3.5 goals in a soccer match, no team is going to score half of a goal.
So the inclusion of the half goal means that a result (win or loss) will happen on the bet. However, you will see straight whole-number spread options too. Maybe it is a simple -4 on the Atlanta Falcons to win.
If they were to win the match 20-16, a margin of exactly four points, then that the spread wasn't covered. It wasn't lost either.
A push results in the stake being refunded, because, on the other side, their opponents didn't cover the +4 spread.
Note that some bookmakers may have 'ties win' or 'ties lose' on markets to avoid a push and have the bet settled.
What is covering the spread?
Covering the spread is a term used to describe a team doing enough to cover whatever the spread is on them.
Spread Betting Made Easy
This simply means that if you have a team at a -3.5 point spread, they would cover that spread if they were to win by at least four points.
If a team was at +3.5 points then they would cover the spread if they didn't get beaten by anything more than three points. It's just a betting phrase determining if your bet won or not.
Does overtime count in a point spread?
If you bet on England to beat Germany in the World Cup Final (90 minutes) and the game is tied, what happens to your stake? It's lost.
Even if England won in extra time, your initial bet only covered the regulation 90 minutes. It's different with spread betting. The major points spread sports in the world, hands down, are American Football, Ice Hockey and Basketball and if any went to overtime then your spread bet would still be active.
Is Forex Spread Betting?
No. Forex is its own thing. It is buying and selling currency at the same time. You make a currency pair when you do that.
Spread Betting Basics Vs
Forex is subject to taxation, spread betting is not. But you can do spread betting on Forex markets.
The advantage of going to a spread betting broker means that you can bet on the Forex without doing Forex directly. You could simply spread bet on the spread of the value of a currency pair to go up or down.
Is Spread Betting taxed?
One of the appeals of Spread Betting in the UK is that profits don't have to be declared to HMRC. So whatever you get to make on spread betting you are going to get to keep.
That is of course unless you put a big sum somewhere where it earns interest and then you would have to pay tax on that.
Spread Betting Basics Rules
Want to learn more about betting? Check out some of our other beginner guides.

